8618566785362 8618566785362 8618566785362 phoenix08@bbamachine.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
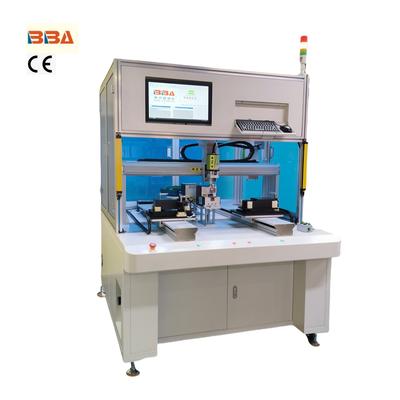

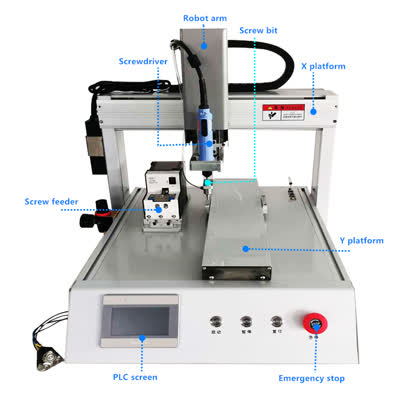
In the realm of industrial automation, screw assembly machines play a pivotal role in streamlining manufacturing processes. A fully automatic screw assembly machine is designed to handle high-volume production with precision, efficiency, and minimal human intervention. Understanding the key components of such a machine can provide valuable insights into how automation enhances productivity. Below, we delve into the essential components that make up a fully automatic screw assembly machine. 1. Screw Feeder The screw feeder is the heart of the assembly machine, responsible for supplying screws in an orderly manner. It typically consists of a vibratory bowl or a linear feeder that orients screws correctly before they are transported to the next stage. Advanced models may include sensors to detect jams or misfeeds, ensuring uninterrupted operation. 2. Screwdriver Unit The screwdriver unit is the component that drives the screws into the workpiece. Depending on the application, it may be an electric, pneumatic, or servo-driven screwdriver. Precision torque control is critical here to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening, which could compromise product quality. 3. Conveyor System A conveyor system transports workpieces through the assembly line, positioning them accurately under the screwdriver unit. Belt-type or chain conveyors are commonly used, and they may incorporate sensors to synchronize the movement of parts with the screwing process. 4. Control Panel The control panel houses the machine's programmable logic controller (PLC) and human-machine interface (HMI). Operators can configure settings such as torque, speed, and screwing sequences through the HMI, while the PLC ensures all components operate in harmony. 5. Vision System (Optional) For high-precision applications, a vision system may be integrated to verify screw placement and detect defects. Cameras and image-processing software analyze each screw insertion to ensure consistency and adherence to quality standards. 6. Sensors and Safety Mechanisms Sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the machine's operation. Proximity sensors, torque sensors, and photoelectric detectors help prevent errors and ensure safe operation. Safety mechanisms, such as emergency stop buttons and protective barriers, safeguard operators from accidental injuries. 7. Hopper or Storage Unit A hopper or storage unit holds a large quantity of screws, replenishing the feeder as needed. This component minimizes downtime by ensuring a continuous supply of screws during extended production runs. Conclusion A fully automatic screw assembly machine is a sophisticated system composed of multiple integrated components, each serving a specific function to ensure efficient and precise screw fastening. By leveraging automation, manufacturers can achieve higher output, reduce labor costs, and maintain consistent product quality. Investing in such machinery is a step toward optimizing production lines for competitive advantage. Product Name Applicable industries Inline Screw Locking System Automotive Electronics Assembly
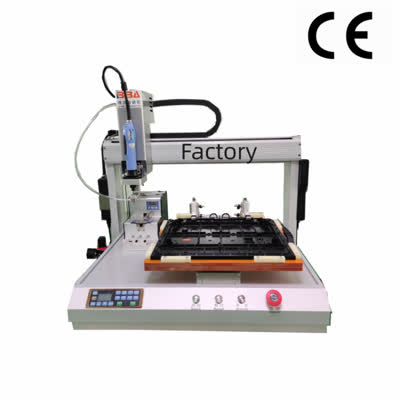

Product Name Applicable industries Screw Fastening Unit Security Equipment Manufacturing A Beginner’s Guide to Multi-Axis Screw Fastening Machines Multi-axis screw fastening machines are revolutionizing industrial automation by offering precision, speed, and flexibility in assembly processes. Whether you're new to automated fastening or looking to optimize production, understanding these machines is essential for modern manufacturing. This guide covers the basics of multi-axis screw fastening technology, its advantages, and key considerations for implementation. What Are Multi-Axis Screw Fastening Machines? These machines are designed to drive screws into multiple points on a workpiece simultaneously or sequentially, using multiple independent axes. Unlike single-axis machines, they can handle complex assemblies with varying screw positions, angles, and torque requirements. Equipped with robotic arms or spindle arrays, they adapt to diverse production needs while maintaining high accuracy. Key Advantages Increased Productivity: Multiple screws are fastened in a single cycle, reducing cycle times. Consistency: Programmable torque and angle settings ensure uniform fastening quality. Flexibility: Easily reprogrammable for different product designs or screw patterns. Reduced Labor Costs: Automates repetitive tasks, minimizing human intervention. Applications These machines excel in industries like automotive, electronics, and appliance manufacturing, where high-volume screw fastening is critical. They’re ideal for assembling circuit boards, engine components, or consumer products with intricate screw layouts. Implementation Tips Assess Workpiece Requirements: Determine screw sizes, depths, and material compatibility. Choose the Right Configuration: Select axes count (2-axis to 6-axis) based on complexity. Integrate Sensors: Use vision systems or force feedback to detect misalignments. Prioritize Maintenance: Regular calibration ensures long-term accuracy. By leveraging multi-axis screw fastening machines, manufacturers can achieve faster, error-free assembly lines. As automation advances, adopting these systems becomes a competitive necessity—not just an option.
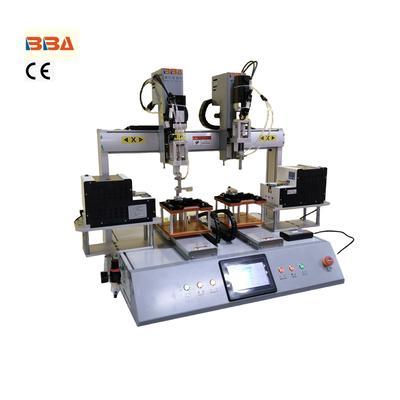

Product Name Applicable industries Desktop Screwdriver Robot Automotive Electronics Assembly The industrial automation sector is witnessing a significant surge in demand for automated fastening systems, driven by the need for precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing processes. As industries increasingly embrace automation, the role of advanced fastening solutions has become pivotal in ensuring seamless operations across assembly lines, automotive production, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. Automated fastening systems are designed to enhance productivity by reducing human error and speeding up production cycles. These systems incorporate advanced technologies such as robotics, torque control, and vision systems to deliver consistent and reliable fastening performance. The ability to precisely control torque and alignment ensures high-quality joints, minimizing the risk of product defects and recalls. One of the key drivers behind the growing demand for automated fastening solutions is the rise of smart factories. Industry 4.0 has paved the way for interconnected production environments where data-driven decision-making is paramount. Automated fastening systems equipped with IoT capabilities can monitor and adjust parameters in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and predictive maintenance. This reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment, contributing to long-term cost savings. The automotive industry, in particular, has been a major adopter of automated fastening technologies. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, with its emphasis on lightweight materials and complex assembly requirements, has further accelerated the adoption. Automated systems can handle a variety of fastening tasks, from securing battery modules to assembling intricate chassis components, while maintaining stringent safety and quality standards. Beyond automotive, industries such as aerospace and electronics are also leveraging these systems to meet the demands of miniaturization and high-precision assembly. The ability to work with diverse materials, including composites and delicate substrates, makes automated fastening indispensable in these sectors. Additionally, labor shortages and the need for lean manufacturing practices are pushing companies to invest in automation to maintain competitiveness. The future of automated fastening systems lies in continuous innovation. Emerging trends such as cobots (collaborative robots) and AI-driven quality assurance are set to revolutionize the field. These advancements will further enhance flexibility, allowing systems to adapt to varying production needs while maintaining high accuracy and reliability. In conclusion, the global demand for automated fastening systems is poised for sustained growth as industries prioritize efficiency, quality, and scalability. Businesses that invest in these cutting-edge solutions today will be well-positioned to lead in the era of advanced manufacturing.
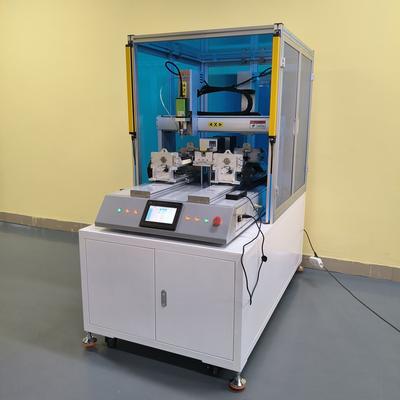

Product Name Applicable industries Automatic Screw Feeder Smart Wearables Production In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, speed and precision are paramount for optimizing production efficiency. High-speed screw locking robots have emerged as a game-changing solution for assembly lines, delivering unparalleled performance in fastening applications. This article explores the advanced technology powering these robotic systems and their transformative impact on industrial automation. At the core of high-speed screw locking robots lies a sophisticated motion control system. These robots employ precision servo motors combined with advanced motion algorithms to achieve rapid positioning with micron-level accuracy. The integration of real-time feedback mechanisms ensures consistent torque application during the fastening process, preventing both under-tightening and material damage from excessive force. Modern screw locking robots feature intelligent vision guidance systems that enable them to locate screw holes with exceptional precision. Using high-resolution cameras and machine vision algorithms, these systems can compensate for minor part variations and maintain optimal alignment throughout the fastening cycle. This capability significantly reduces the need for costly fixturing while improving overall process reliability. The drive mechanisms in these robots utilize brushless DC motors with harmonic drive reducers to deliver the perfect balance of speed and torque. Advanced vibration-damping technology minimizes oscillations during rapid movements, allowing for screw insertion speeds exceeding 5 screws per second in some configurations. This remarkable speed is achieved without compromising placement accuracy or tightening quality. Smart screw feeding systems complement the robot's mechanical performance. These feeders incorporate unique separation and orientation technologies to ensure a continuous supply of properly aligned screws to the locking head. Sophisticated sensors monitor the feeding process, instantly detecting and correcting any jams or misalignments to prevent production interruptions. Modern high-speed screw locking robots offer remarkable flexibility through advanced programming interfaces. Operators can easily adjust parameters such as tightening torque, insertion speed, and depth for different product variants. Some systems even feature self-learning capabilities that optimize these parameters over time based on historical performance data. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies has further enhanced these robotic systems. Built-in connectivity allows for real-time monitoring of key performance metrics, predictive maintenance alerts, and seamless integration with factory-wide control systems. This data-driven approach maximizes uptime and provides valuable insights for continuous process improvement. As manufacturing requirements continue to evolve, high-speed screw locking robots are being adapted to handle increasingly complex tasks. Some advanced models now incorporate collaborative robot technology, enabling safe operation alongside human workers in hybrid assembly environments. Others feature multi-head configurations that can drive different types of fasteners simultaneously, further boosting productivity. The future of screw locking technology lies in continued improvements in speed, adaptability, and intelligent capabilities. Emerging developments in artificial intelligence promise even more autonomous operation, with robots capable of self-adjusting to new product designs and production conditions. As these technologies mature, high-speed screw locking robots will play an even greater role in shaping the factories of tomorrow.

Programming Servo Screw Drivers for Different Screw Patterns Industrial automation has revolutionized manufacturing, with servo screwdrivers playing a pivotal role in assembly lines. These precision tools offer unmatched control over torque, speed, and angle, ensuring consistent and reliable fastening. However, optimizing servo screwdrivers for various screw patterns requires careful programming to maximize efficiency and minimize errors. The foundation of effective programming lies in understanding the screw pattern requirements. Linear patterns, circular arrangements, and staggered configurations each demand specific approaches. For linear patterns, programmers must define the pitch distance between screws and implement precise positioning logic. Circular patterns require angular calculations and radius parameters to maintain uniform spacing. Torque profiling is another critical aspect of servo screwdriver programming. Different materials and screw sizes require varying torque values to achieve optimal clamping force without damaging components. Modern servo systems allow for dynamic torque adjustment during the fastening process, enabling smooth transitions from rapid approach to final tightening. Advanced programming techniques include implementing error detection routines. These can identify cross-threading, stripped screws, or misaligned parts by monitoring torque curves and rotational position. When anomalies are detected, the system can automatically initiate corrective procedures or halt operations to prevent further damage. Integration with robotic systems adds another layer of complexity to programming servo screwdrivers. Coordinate transformations must be precisely mapped between the robot's movement and the screwdriver's operation. This requires synchronization of motion profiles and careful timing to ensure the tool engages properly with each fastener location. For complex assembly operations, programming sequences may involve multiple tools working in coordination. This demands sophisticated communication protocols between devices and careful sequencing to prevent collisions while maintaining optimal cycle times. Simulation software can help verify these programs before implementation on the production floor. As industrial automation continues to evolve, programming methods for servo screwdrivers are becoming more intuitive. Many modern systems offer graphical interfaces that simplify the creation of complex patterns, with drag-and-drop functionality for positioning and parameter setting. However, a deep understanding of the underlying principles remains essential for troubleshooting and optimization. The future of servo screwdriver programming lies in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Predictive algorithms may soon automate the optimization of screw patterns and fastening parameters based on real-time performance data, further enhancing quality and productivity in automated assembly processes. Product Name Applicable industries Smart Screw Driving Machine Smart Wearables Production
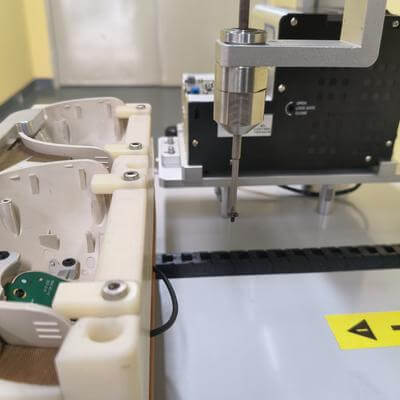

In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. One of the most significant advancements in production automation is the widespread adoption of automatic screw locking machines. These high-precision tools have become indispensable for industries ranging from electronics and automotive to medical devices and consumer goods. Let's explore the key reasons behind their surging global demand. Unmatched Precision and ConsistencyManual screw driving is prone to human errors such as over-tightening, under-tightening, or cross-threading - defects that can compromise product reliability. Automatic screw locking machines eliminate these issues with micron-level accuracy, applying perfect torque every time. This consistency is crucial for industries where tiny fasteners must meet strict quality standards, particularly in miniaturized electronics and sensitive medical equipment. Dramatic Productivity GainsThese machines operate at speeds no human operator can match. A single automated unit can typically drive 30-60 screws per minute with zero fatigue, compared to 8-12 screws manually. For high-volume manufacturers, this translates to throughput increases of 400% or more. The time saved on each screw accumulates into massive annual productivity gains, allowing companies to scale operations without proportionally increasing labor costs. Labor Cost ReductionWith rising wages worldwide and persistent skilled labor shortages, automation provides a compelling ROI. Automatic screw locking systems require minimal supervision - one technician can often oversee multiple machines. Over a 3-year period, companies typically recover their investment through reduced direct labor costs and quality-related savings, while gaining predictable, scalable production capacity. Advanced Data IntegrationModern models feature IoT connectivity, recording every screw's torque curve and feeding data into quality management systems. This creates an auditable trail for compliance-sensitive industries and enables predictive maintenance by tracking tool wear patterns. Some systems even use AI to self-correct torque parameters based on material variances detected during operation. Worker Safety ImprovementsRepetitive screw driving ranks among the top causes of workplace musculoskeletal disorders. Automation removes this ergonomic hazard while also reducing injury risks from tool slippage or flying debris. The newest safety-rated collaborative models can operate alongside humans without protective barriers, combining automation flexibility with manual assembly advantages. Customization CapabilitiesUnlike rigid automation of the past, today's screw locking solutions offer remarkable adaptability. Quick-change tooling heads allow single machines to handle multiple screw types and sizes. Vision-guided robots can locate and fasten screws on irregular surfaces, while flexible feeding systems accommodate anything from M0.6 micro-screws to large structural bolts with equal precision. As global manufacturers face intensifying pressure to deliver higher quality at lower costs with shrinking timelines, automatic screw locking technology has evolved from a luxury to a necessity. The combination of precision engineering, smart connectivity, and flexible automation ensures these systems will remain at the core of Industry 4.0 manufacturing strategies worldwide. Product Name Applicable industries Screw Locking Robot Industrial Control Panel Assembly
The servo screw technology market is a rapidly evolving sector, driven by advancements in automation and precision engineering. As industries increasingly demand higher accuracy, efficiency, and reliability, selecting the right servo screw system becomes critical for optimal performance. This article compares leading brands in servo screw technologies, highlighting key features, innovations, and applications that set them apart. One of the primary considerations in servo screw technology is precision. High-end systems now offer micron-level accuracy, ensuring consistent performance in applications requiring tight tolerances. These systems integrate advanced feedback mechanisms, such as optical encoders and resolvers, to maintain precise positioning and minimize backlash. The result is improved repeatability, even in high-speed operations. Durability is another critical factor. Modern servo screw systems are designed with high-grade materials, including hardened steel and specialized coatings, to withstand harsh industrial environments. Corrosion resistance, reduced wear, and extended service life are standard features in top-tier models. Additionally, innovative lubrication systems ensure smooth operation under heavy loads and continuous use. Energy efficiency is a growing priority in industrial automation. Leading servo screw technologies incorporate regenerative braking and optimized motor designs to minimize power consumption. By reducing energy waste, these systems lower operational costs and align with sustainability goals. Some models also feature smart diagnostics, enabling predictive maintenance to prevent unexpected downtime. Integration capabilities are equally important. The best servo screw systems offer seamless compatibility with PLCs, HMIs, and other automation components. Open communication protocols, such as EtherCAT and Profinet, facilitate easy setup and real-time monitoring. This interoperability ensures smooth workflows in complex manufacturing environments. In conclusion, selecting the right servo screw technology involves evaluating precision, durability, energy efficiency, and integration features. By understanding these key factors, manufacturers can make informed decisions to enhance their automation processes and stay competitive in a dynamic industry. Product Name Applicable industries Dual Head Screwdriver Telecommunication Equipment Assembly
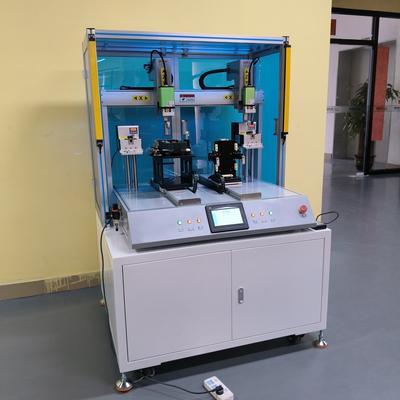

Product Name Applicable industries CNC Screw Fastener LED Lighting Industry In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, efficiency and precision are more critical than ever. One of the most significant advancements helping factories achieve these goals is the adoption of automatic screw locking machines. These innovative tools are revolutionizing assembly lines, offering unparalleled speed, consistency, and reliability. But why are more factories making the switch? Let’s explore the key reasons behind this growing trend. Enhanced Productivity Manual screw tightening is time-consuming and labor-intensive, often becoming a bottleneck in production. Automatic screw locking machines streamline the process, completing tasks in a fraction of the time. With high-speed operation and minimal downtime, these machines significantly boost productivity, allowing factories to meet increasing demand without compromising quality. Unmatched Precision Human error is inevitable in manual screw tightening, leading to inconsistencies such as over-tightening or under-tightening. Automatic screw locking machines eliminate this variability by applying the exact torque required for each screw. This precision ensures uniform product quality, reduces defects, and enhances the longevity of assembled products. Labor Cost Savings Labor costs are a significant expense for manufacturing facilities. By automating the screw locking process, factories can reduce their reliance on manual labor, reallocating workers to more complex tasks that require human expertise. This not only cuts costs but also optimizes workforce efficiency. Improved Worker Safety Repetitive tasks like screw tightening can lead to musculoskeletal disorders and fatigue among workers. Automatic screw locking machines take over these repetitive motions, reducing the risk of workplace injuries. A safer work environment not only protects employees but also minimizes downtime due to health-related absences. Scalability and Flexibility Modern automatic screw locking machines are highly adaptable, capable of handling a wide range of screw sizes and materials. Whether a factory produces electronics, automotive parts, or consumer goods, these machines can be customized to fit specific needs. This scalability makes them a future-proof investment for growing businesses. Data Tracking and Quality Control Many automatic screw locking machines come equipped with advanced sensors and software that monitor each tightening operation. This data can be used for real-time quality control, ensuring every product meets stringent standards. Additionally, tracking performance metrics helps identify potential issues before they escalate, further enhancing operational efficiency. As industries continue to embrace automation, the shift toward automatic screw locking machines is a natural progression. Their ability to enhance productivity, precision, and safety while reducing costs makes them an indispensable tool for modern factories. Investing in this technology not only keeps businesses competitive but also paves the way for smarter, more efficient manufacturing processes.