8618566785362 8618566785362 8618566785362 phoenix08@bbamachine.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search

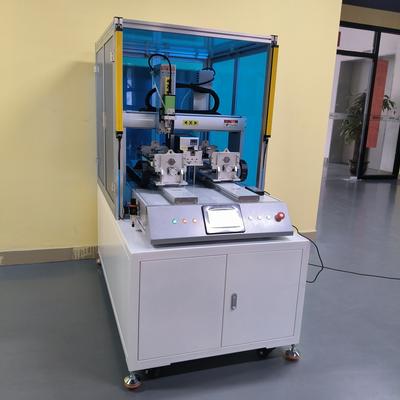
Product Name Applicable industries Servo Screwdriver Robot PCB and Circuit Board Assembly body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; margin: 20px; color: #333; } h1 { color: #0056b3; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 15px; } p { margin-bottom: 15px; } strong { color: #0056b3; } Minimizing Human Error with Desktop Screw Robots In the fast-paced world of industrial manufacturing, precision and consistency are paramount. Even the smallest error in assembly can lead to significant product defects, costly rework, and potential safety hazards. For decades, the repetitive task of screw driving has been a primary source of these errors, reliant on the focus and endurance of human operators. Today, a new era of automation is addressing this challenge head-on. Desktop screw robots are emerging as a transformative solution, fundamentally minimizing human error and elevating production quality to unprecedented levels. Human operators, despite their best efforts, are susceptible to fatigue, distraction, and variations in technique. These factors can lead to a range of common issues in manual screw fastening: cross-threading, under-torquing, over-torquing, and even forgotten screws. Each of these mistakes can compromise the structural integrity and functionality of the final product. The consequences are not merely financial; they can damage a brand's reputation for reliability. This is where desktop screw robots excel. These compact, self-contained automated systems are designed to perform screw driving tasks with machine-like precision, repeatedly and without deviation. Equipped with advanced vision systems and sensitive torque feedback, these robots can precisely locate screw holes and drive each fastener to the exact specified torque value every single time. This eliminates the variability inherent in manual processes, ensuring every product coming off the line meets identical high-quality standards. The integration of these robots into existing production workflows is remarkably straightforward. Their desktop format allows them to be deployed directly on the assembly line, right beside human workers, without the need for massive factory floor renovations. This makes automation accessible not only for high-volume production but also for smaller batch sizes and mixed-product assembly. Operators can be quickly trained to oversee multiple robots, shifting their role from repetitive manual labor to more value-added tasks like quality inspection, machine supervision, and process optimization. Beyond impeccable quality control, the benefits of deploying desktop screw robots are multifaceted. Companies report a substantial increase in throughput, as these systems can operate consistently at speeds difficult for humans to maintain over a full shift. Furthermore, they significantly enhance workplace safety by reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries associated with manual screw driving, creating a safer and more ergonomic environment for employees. In conclusion, the move towards automation is no longer just about increasing speed; it's about guaranteeing precision and building inherent quality into the manufacturing process. Desktop screw robots represent a critical step in this journey. By virtually eliminating human error in a fundamental assembly task, they empower manufacturers to achieve new heights of product consistency, operational efficiency, and workplace safety. As this technology continues to evolve and become even more sophisticated, it is set to become an indispensable cornerstone of the modern, error-free factory floor.

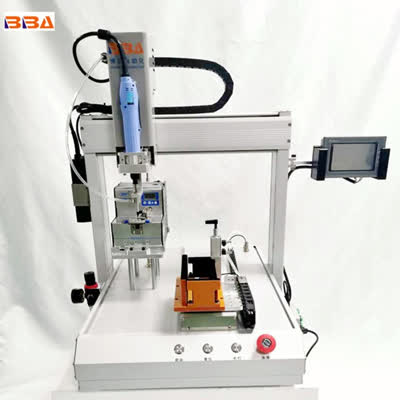
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; color: #333; margin: 20px; } h1 { color: #0056b3; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 20px; } h2 { color: #004a99; font-size: 22px; margin-top: 25px; margin-bottom: 15px; } p { margin-bottom: 15px; text-align: justify; } ul { margin-bottom: 15px; padding-left: 20px; } li { margin-bottom: 8px; } strong { color: #004a99; } Customizing Your Automatic Screw Locking Machine for Specific Products In the competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, efficiency and precision are not just goals—they are necessities. One of the most critical processes in assembly lines is screw fastening, a task that, if done manually, can be time-consuming, prone to error, and physically demanding for workers. Automatic screw locking machines have revolutionized this aspect of production, offering unparalleled speed, consistency, and reliability. However, the true power of these machines is fully realized only when they are meticulously customized to handle the specific products and unique requirements of your assembly process. Off-the-shelf solutions provide a solid foundation, but customization is the key to unlocking maximum productivity, quality, and return on investment. Understanding the Need for Customization Every product is unique. It has a distinct geometry, weight, material composition, and set of technical specifications. The screws used can vary dramatically in size, head type, torque requirements, and material. An automatic screw locking machine designed for assembling large automotive components will be vastly different from one needed for delicate electronic devices like smartphones or medical sensors. A one-size-fits-all approach simply cannot address these nuances effectively. Customization ensures that the machine integrates seamlessly into your existing production line, handles your specific components gently yet firmly, and applies the exact torque required every single time, eliminating the risks of cross-threading, stripping, or under-tightening. Key Areas of Customization Tailoring an automatic screw locking machine involves a holistic approach, focusing on several critical aspects of its operation and integration. Feeding System and Screw Presentation: The system that feeds and presents screws to the driver bit must be configured for your specific screw type. This includes the design of the bowl feeder, tracks, and escapement mechanism to ensure smooth, jam-free delivery of screws, even if they are very small, have unusual head styles, or are made of non-standard materials. Torque and Angle Control: Precision fastening is paramount. The machine's controller must be programmed with the exact torque and angle parameters for each screw in your product. This is especially critical for products where a specific clamp load is required for safety or performance, such as in aerospace components or medical devices. End-Effector and Tooling: The driver head, often mounted on a robotic arm or a multi-axis system, must be equipped with the correct bit and may require custom-designed fixtures or jaws to hold your product securely in place without causing any cosmetic or structural damage. Vacuum suction or soft-touch mechanisms can be added for handling fragile products. Integration with Automation: The machine must communicate flawlessly with other equipment on your line, such as conveyors, pick-and-place robots, or vision inspection systems. Custom software interfaces and communication protocols (like PLC I/O or Ethernet/IP) are developed to create a synchronized and efficient workflow. Safety and Ergonomics: Custom guarding, light curtains, and safety interlocks are implemented based on the machine's location and the operators' interaction with it, ensuring a safe working environment that complies with all relevant regulations. The Customization Process: A Collaborative Effort Successfully customizing an automatic screw locking machine is a collaborative journey between your engineering team and our application experts. It typically begins with a detailed analysis of your product, samples, and assembly drawings. We then conduct thorough tests in our lab using your actual components to define the optimal configuration. This iterative process allows us to prototype solutions, validate performance, and fine-tune the machine until it meets your exact quality and throughput targets. The result is a turnkey solution that feels like it was built from the ground up just for your factory. Unlocking Long-Term Value Investing in a customized automatic screw locking machine is an investment in the future of your production. Beyond the immediate gains in speed and quality, it offers remarkable long-term value. A perfectly tailored machine reduces downtime caused by jams or errors, minimizes scrap and rework, and lowers the total cost of ownership. Furthermore, a well-designed system is often adaptable, allowing for future changes to your product design without requiring a complete machine overhaul. In an era where agility is crucial, this flexibility provides a significant competitive advantage. Ultimately, customizing your automatic screw locking machine transforms it from a generic piece of equipment into a strategic asset. It becomes an integral part of your quality assurance system, a driver of your production efficiency, and a reliable partner in building your products to the highest possible standard. Product Name Applicable industries Servo Screwdriver Robot Electric Bicycle Assembly

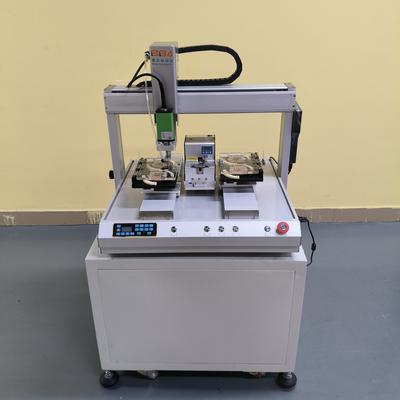
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; color: #333; margin: 20px; } h1 { color: #2c3e50; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 10px; } h2 { color: #34495e; font-size: 22px; margin-top: 25px; margin-bottom: 10px; } p { margin-bottom: 15px; text-align: justify; } .highlight { background-color: #f8f9fa; padding: 15px; border-left: 4px solid #3498db; margin: 20px 0; } .region { font-weight: bold; color: #2980b9; } Regional Differences in Screw Locking Robot Utilization The adoption of screw locking robots in industrial automation varies significantly across global regions, reflecting diverse economic priorities, labor dynamics, and technological readiness. These differences highlight how manufacturers tailor automation strategies to local conditions while addressing universal demands for precision, efficiency, and quality. North America: Precision and High-Value Manufacturing In North America, screw locking robots are predominantly deployed in high-value industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. The region’s focus on stringent quality standards and reduced production errors drives adoption. Manufacturers leverage these robots to ensure consistent torque accuracy and traceability, critical for compliance and liability reduction. The high cost of labor and emphasis on reshoring production further accelerate integration, with robots often deployed in collaborative cells alongside human operators. Europe: Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability European manufacturers prioritize screw locking robots for their ability to enhance process standardization and meet rigorous regulatory requirements. Industries like automotive, medical devices, and machinery invest in these systems to achieve flawless assembly records, reducing recalls and waste. The region’s strong emphasis on sustainability aligns with the robots’ role in minimizing rework and material usage. Additionally, integration with Industry 4.0 frameworks allows real-time monitoring and data analytics, supporting smart factory initiatives. Asia-Pacific: Scalability and Labor Optimization The Asia-Pacific region leads in volume-driven adoption, particularly in consumer electronics, automotive, and semiconductor sectors. Countries with large manufacturing bases, such as China, Japan, and South Korea, utilize screw locking robots to overcome labor shortages and maintain high throughput. The focus is on scalability and rapid deployment in assembly lines, where robots excel in high-speed, repetitive tasks. Cost-effectiveness and flexibility in production layout are key considerations, with manufacturers often opting for modular automation solutions. Emerging Markets: Gradual Integration and Cost Sensitivity In developing regions like Latin America and Southeast Asia, adoption is gradual due to cost constraints and less mature automation infrastructure. Screw locking robots are typically introduced in export-oriented industries or multinational subsidiaries where global standards apply. These regions prioritize affordable, easy-to-deploy systems that offer quick returns on investment. As labor costs rise and technology becomes more accessible, utilization is expected to grow, focusing on hybrid automation models. The regional disparities in screw locking robot utilization underscore the importance of context-driven automation solutions. While advanced economies emphasize precision and compliance, emerging markets focus on scalability and cost-efficiency. Understanding these differences enables manufacturers to align automation investments with regional realities, ensuring optimal performance and competitiveness. As technology evolves and becomes more accessible, these regional gaps are likely to narrow, fostering a more interconnected and efficient global industrial landscape. The future will see increased adaptability in robotic systems, allowing seamless integration across diverse manufacturing environments worldwide. Product Name Applicable industries Inline Screw Locking System Smart Wearables Production

Product Name Applicable industries Screw Locking Robot Industrial Control Panel Assembly In the world of industrial manufacturing, maintaining precision and reliability across multiple production shifts is a significant challenge. One critical area where consistency is paramount is screw locking operations. Whether in automotive assembly, electronics manufacturing, or heavy machinery production, the integrity of screw fastening can impact product quality, safety, and performance. Variations in torque, angle, or sequencing between shifts can lead to inconsistencies that result in product defects, equipment failures, or even safety hazards. To achieve uniformity in screw locking processes, manufacturers must address several key factors. First, standardized operating procedures are essential. Clearly documented guidelines for screw locking parameters—such as torque values, tightening sequences, and tool calibration—ensure that every operator, regardless of shift, follows the same protocol. This reduces human error and promotes repeatability. Another crucial element is the use of advanced automated screw locking systems. Modern solutions incorporate real-time monitoring and data logging capabilities, allowing supervisors to track performance metrics across shifts. These systems can detect deviations from predefined parameters and alert operators immediately, preventing inconsistent applications. Additionally, automated tools can be programmed to enforce precise torque and angle settings, eliminating variability caused by manual operations. Training and communication also play vital roles in maintaining consistency. Regular cross-shift training sessions ensure that all team members are up-to-date with the latest procedures and technologies. Open communication channels between shift leaders help address any discrepancies quickly, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Furthermore, integrating IoT-enabled devices into screw locking systems offers a proactive approach to consistency. Sensors embedded in tools collect data on each fastening operation, which is then analyzed to identify trends or anomalies across shifts. This data-driven insight enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and ensuring that equipment operates at peak performance consistently. In conclusion, achieving consistency in screw locking across multiple shifts requires a combination of standardized processes, advanced automation, ongoing training, and data integration. By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can enhance product quality, optimize efficiency, and maintain a high level of reliability throughout their operations.
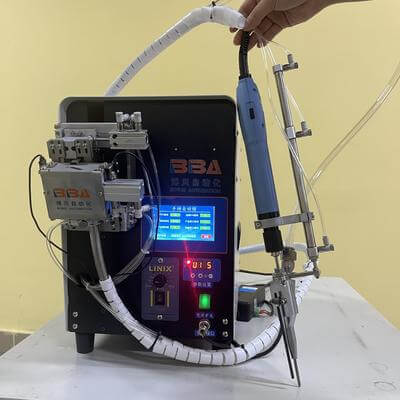
Product Name Applicable industries Desktop Screwdriver Robot Home Appliance Production In the world of industrial automation, reliability is everything. From assembly lines to robotic systems, every component must function as intended to ensure seamless operations. One common yet often overlooked issue is loose screws. A loose screw might seem like a minor problem, but it can lead to significant downtime, reduced product quality, and even safety hazards. Fortunately, screw locking automation offers a modern, efficient, and highly reliable solution to this age-old challenge. Screw locking automation involves the use of advanced machinery designed to apply locking mechanisms—such as threadlockers, lock washers, or self-locking screws—consistently and accurately. These systems are integrated into production lines to ensure that every screw is secured to the required specification, eliminating human error and variability. The automation process typically includes precision dispensing, tightening, and verification steps, all performed at high speed and with repeatable accuracy. One of the key benefits of using automated screw locking systems is the enhancement of product durability. By ensuring that screws remain firmly in place, these systems prevent loosening caused by vibrations, thermal cycles, or dynamic loads. This is particularly critical in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where failure of a single component can have cascading effects. Another advantage is the significant reduction in maintenance and warranty costs. Products assembled with automated screw locking are less likely to require repairs or recalls due to fastener-related issues. This not only saves money but also protects brand reputation by delivering higher quality and more reliable products to end-users. Implementing screw locking automation also boosts overall production efficiency. Manual application of threadlockers or other locking methods is time-consuming and prone to inconsistency. Automated systems, on the other hand, can process hundreds or even thousands of screws per hour with uniform quality, integrating seamlessly with existing assembly processes. Many systems also feature real-time monitoring and data logging, providing valuable insights for process optimization and quality assurance. When selecting a screw locking automation solution, it is important to consider factors such as the type of locking mechanism required, the production volume, and the compatibility with existing equipment. Modern systems offer flexibility to handle various adhesives, patches, or mechanical lockers, and can be customized to meet specific operational needs. In conclusion, screw locking automation represents a smart investment for any industrial automation-focused company looking to improve product reliability, reduce costs, and enhance manufacturing efficiency. By addressing the problem of loose screws with precision and consistency, these systems help build a stronger foundation for quality and performance in industrial applications.

body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; margin: 20px; } h1 { color: #2c3e50; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 20px; } h2 { color: #34495e; font-size: 22px; margin-top: 25px; margin-bottom: 15px; } p { margin-bottom: 16px; text-align: justify; } ul { margin-bottom: 16px; padding-left: 20px; } li { margin-bottom: 8px; } .highlight { background-color: #f8f9fa; padding: 15px; border-left: 4px solid #3498db; margin: 20px 0; } Basic Working Principles of Automatic Screw Assembly Equipment In the modern industrial landscape, automation has become a cornerstone for enhancing productivity, ensuring consistent quality, and optimizing operational efficiency. Among the various automated systems widely adopted in manufacturing, automatic screw assembly equipment plays a pivotal role in numerous assembly lines. This technology is designed to handle the repetitive and precise task of driving screws without human intervention, significantly speeding up production while reducing errors and labor costs. Understanding the fundamental working principles of these systems is essential for appreciating their value and functionality in industrial settings. Core Components and Their Functions Automatic screw assembly systems are integrated solutions comprising several key components that work in unison. The primary elements include a screw feeder, a drive unit, a controller, and often a robotic arm or positioning system. The screw feeder is responsible for storing a bulk quantity of screws and orienting them correctly one by one. It typically uses a vibratory bowl or a blade mechanism to align the screws and present them in a predefined position for pickup. The drive unit, commonly an electric or pneumatic screwdriver, is the tool that actually fastens the screw into the target workpiece. It is equipped with a clutch and sensors to control torque and depth, ensuring each screw is driven with precise force to meet stringent quality standards. The controller, usually a programmable logic controller (PLC) or a dedicated microprocessor, acts as the brain of the system. It coordinates the actions of the feeder and the drive unit, manages input from sensors, and can be programmed for various parameters such as screw count, torque settings, and assembly sequence. Advanced controllers also facilitate integration with broader production line networks for data tracking and process monitoring. Lastly, a positioning system guides the drive unit to the exact location where the screw needs to be inserted. This can be achieved through fixed mechanical guides, multi-axis robotic arms, or sophisticated vision systems that identify and align with the target point accurately. The Operational Workflow The operation of an automatic screw assembly machine follows a streamlined, cyclic process. It begins when the workpiece is positioned correctly on the assembly fixture or conveyor. The controller then initiates the cycle, commanding the feeder to deliver a single screw to the pickup point. Using a vacuum suction nozzle or a mechanical gripper, the drive unit retrieves the screw from the feeder. The positioning system moves the drive unit to the predetermined coordinates above the workpiece. The screwdriver descends, engages the screw head, and rotates it into the pre-tapped hole or directly into the material, applying the programmed torque until the screw is securely fastened. Sensors continuously monitor the process to detect any anomalies, such as cross-threading, missing screws, or incorrect torque, immediately halting operation or alerting operators if a fault is identified. This entire sequence is executed within seconds, demonstrating high efficiency and repeatability. The integration of automatic screw assembly equipment brings transformative benefits to manufacturing operations. It not only accelerates assembly speeds far beyond manual capabilities but also drastically reduces the physical strain on workers and minimizes the risk of repetitive strain injuries. Moreover, the data collected by these systems provides valuable insights for process optimization and quality assurance, making them an indispensable asset in smart factories and high-volume production environments. Advantages in Industrial Applications The adoption of automatic screw assembly technology offers numerous advantages that directly impact the bottom line. Firstly, it ensures unparalleled consistency and quality in fastening operations. Every screw is driven with identical torque and depth, eliminating human variability and preventing issues like over-tightening or under-tightening, which can lead to product failures. Secondly, these systems dramatically increase output rates, capable of installing hundreds or even thousands of screws per hour without fatigue. This is particularly crucial in industries such as electronics, automotive, and appliance manufacturing, where the number of screws per product can be substantial. Furthermore, automation enhances workplace safety by removing operators from potentially hazardous tasks and reduces the overall cost of labor by reallocating human resources to more value-added activities like supervision and maintenance. The flexibility of modern equipment allows for quick changeovers between different products and screw sizes, making them suitable for both mass production and batch manufacturing. With the ongoing advancements in machine vision and artificial intelligence, future generations of automatic screw assembly systems are expected to become even more adaptive, capable of handling complex assemblies with minimal programming effort. In conclusion, automatic screw assembly equipment represents a sophisticated synergy of mechanical engineering, control systems, and sensor technology. Its basic principle revolves around automating a simple yet critical task to achieve levels of speed, precision, and reliability that are unattainable through manual methods. As industries continue to strive for greater efficiency and quality, the role of such automated solutions will undoubtedly become more prominent, driving innovation and competitiveness in the global market. Product Name Applicable industries CNC Screw Fastener Telecommunication Equipment Assembly

Smart Alarms and Sensors in Desktop Screwdriver Robots body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; margin: 20px; color: #333; } h1 { color: #0056b3; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 20px; } h2 { color: #007bff; font-size: 22px; margin-top: 25px; margin-bottom: 15px; } p { margin-bottom: 15px; text-align: justify; } ul { margin-left: 20px; margin-bottom: 15px; } li { margin-bottom: 8px; } .highlight { background-color: #f8f9fa; padding: 15px; border-radius: 5px; margin: 20px 0; } Smart Alarms and Sensors in Desktop Screwdriver Robots In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, precision and reliability are paramount. Desktop screwdriver robots have emerged as critical tools in assembly lines, electronics manufacturing, and intricate mechanical work. These compact yet powerful systems are designed to handle repetitive fastening tasks with unmatched accuracy. However, the true advancement in their functionality lies in the integration of smart alarms and advanced sensor technology. This innovation not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces downtime and prevents costly errors. The Role of Smart Alarms Smart alarms are intelligent notification systems that proactively monitor the status of desktop screwdriver robots. Unlike traditional alarms that simply alert users to a problem after it occurs, smart alarms use real-time data analytics to predict potential issues before they escalate. For instance, if a robot detects an abnormal torque pattern during screw driving, it can trigger an alarm indicating possible cross-threading or material defects. This allows operators to intervene immediately, preventing defective products and minimizing waste. These alarms are often integrated with visual and auditory signals, such as LED indicators or beeping sounds, ensuring that personnel are promptly aware of any anomalies. Moreover, they can be connected to centralized monitoring systems via IoT platforms, enabling remote notifications and historical data analysis for continuous process improvement. Advanced Sensor Technology Sensors are the eyes and ears of desktop screwdriver robots, providing critical feedback on various parameters. Modern robots are equipped with a suite of sensors, including torque sensors, position encoders, and pressure sensors, which work in tandem to ensure each screw is driven perfectly. Torque Sensors: Measure the rotational force applied during fastening, ensuring it remains within specified tolerances to avoid under or over-tightening. Position Encoders: Provide precise information on the robot’s location, guaranteeing screws are placed accurately even in high-density assemblies. Pressure Sensors: Detect the contact force between the screwdriver bit and the screw head, preventing slippage and damage to components. These sensors continuously feed data to the robot’s control unit, which adjusts operations in real time. For example, if a torque sensor detects resistance beyond predefined limits, the system may automatically recalibrate or halt to avoid stripping the screw. Benefits in Industrial Applications The integration of smart alarms and sensors transforms desktop screwdriver robots from mere tools into intelligent assistants. In electronics manufacturing, where screws are tiny and components fragile, these systems prevent over-torque that could crack circuit boards. In automotive assembly, they ensure consistent torque across multiple fasteners, enhancing product safety and reliability. Key advantages include: Reduced defect rates through real-time monitoring and corrective actions. Increased productivity with minimal manual intervention and downtime. Enhanced traceability with logged data for each fastening operation, useful for quality audits. Improved worker safety by automating hazardous or ergonomically challenging tasks. Future Trends Looking ahead, the convergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning with sensor technology will further revolutionize desktop screwdriver robots. Predictive maintenance algorithms will analyze sensor data to forecast component failures, scheduling repairs before breakdowns occur. Additionally, adaptive learning capabilities will enable robots to self-optimize based on historical performance, achieving even higher levels of precision. In conclusion, smart alarms and sensors are not just add-ons but essential components that elevate desktop screwdriver robots to new heights of intelligence and efficiency. As industries continue to embrace automation, these innovations will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing, making processes smarter, safer, and more sustainable. Product Name Applicable industries Desktop Screwdriver Robot Electric Bicycle Assembly

body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; line-height: 1.6; margin: 20px; color: #333; } h1 { color: #2c5aa0; font-size: 28px; margin-bottom: 20px; } h2 { color: #3a6bb5; font-size: 22px; margin-top: 25px; margin-bottom: 15px; } p { margin-bottom: 15px; text-align: justify; } ul { margin-bottom: 15px; padding-left: 20px; } li { margin-bottom: 8px; } .highlight { background-color: #f0f8ff; padding: 15px; border-radius: 5px; margin: 15px 0; } Environmental Benefits of Automated Screw Tightening In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the push for sustainability is stronger than ever. Manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to minimize their environmental footprint while maintaining high levels of productivity and quality. One often-overlooked area with significant potential for positive environmental impact is the assembly process, specifically screw tightening. The adoption of automated screw tightening systems is not just a step towards enhanced efficiency; it is a leap forward in eco-friendly manufacturing. Reduction in Material Waste Manual screw tightening processes are inherently prone to human error. Over-tightening can strip threads or damage components, while under-tightening can lead to product failures. Both scenarios result in wasted materials—defective parts that must be scrapped and replaced. Automated screw tightening systems apply precise, consistent torque every time, drastically reducing the rate of assembly errors. This precision ensures that components are fastened correctly the first time, minimizing the generation of waste material and conserving the raw resources that would have been used for replacements. Energy Efficiency Modern automated screwdriving solutions are engineered for optimal energy consumption. Unlike continuous manual operation, these systems are designed to operate only when necessary and often incorporate energy-efficient motors and smart controls that reduce idle power draw. Furthermore, by streamlining the assembly process and reducing cycle times, they contribute to lower overall energy usage per unit produced. This increased efficiency translates directly into a smaller carbon footprint for manufacturing facilities. Optimized Resource Utilization The environmental cost of a product extends beyond the factory floor. It includes the energy and resources used to produce and transport components. By drastically improving precision and reducing the defect rate, automated screw tightening helps prevent the waste of these embedded resources. Fewer defective products mean fewer components need to be manufactured and shipped to replace them, saving the energy and emissions associated with additional production and logistics. This creates a more efficient and less wasteful supply chain from start to finish. Long-Term Product Durability and Lifecycle A crucial yet indirect environmental benefit lies in product quality. A product assembled with consistent and accurate torque is inherently more reliable and durable. It is less likely to fail prematurely, which means it won't need to be replaced as quickly. This extended product lifespan is a fundamental principle of sustainability. It reduces the demand for raw materials, energy for manufacturing, and waste generation from discarded goods, contributing to a circular economy model. Conclusion The integration of automated screw tightening technology is a clear demonstration that economic and environmental goals can be perfectly aligned. By enhancing precision, reducing waste, lowering energy consumption, and contributing to longer-lasting products, this automation technology offers a tangible path for manufacturers to improve their sustainability metrics. As industries continue to innovate, embracing such smart technologies will be paramount in building a more efficient and environmentally responsible manufacturing future. Product Name Applicable industries Automatic Screw Feeder Laptop and Tablet Assembly