8618566785362 8618566785362 8618566785362 phoenix08@bbamachine.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
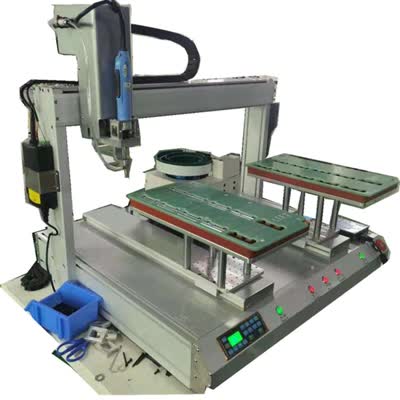

Servo motor screw driving systems are essential components in modern industrial automation, offering precise control over motion and positioning in manufacturing and assembly processes. These systems combine servo motors and screw-driven mechanisms to achieve high accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency in linear and rotational movements. In this article, we explore the fundamentals of servo motor screw driving systems, their key components, and how they benefit various automation applications. What Is a Servo Motor Screw Driving System? A servo motor screw driving system consists of a servo motor coupled with a screw drive mechanism, such as a ball screw or lead screw, to convert rotary motion into linear motion. Servo motors provide controlled movement with high torque and speed, while the screw mechanism ensures smooth and precise linear displacement. These systems are widely used in CNC machines, robotic arms, 3D printers, and automated assembly lines. Key Components of a Servo Motor Screw Driving System 1. Servo Motor – The heart of the system, a servo motor delivers precise rotational motion with feedback control. It adjusts speed and position dynamically, making it ideal for automation tasks requiring high accuracy. 2. Screw Drive Mechanism – Ball screws and lead screws translate the motor's rotary motion into linear movement. Ball screws offer low friction and high efficiency, while lead screws provide cost-effective solutions for less demanding applications. 3. Linear Guide Rails – These support the moving parts, ensuring smooth and stable linear motion with minimal deflection. 4. Feedback Devices (Encoders) – Encoders send real-time position and speed data back to the controller, enabling closed-loop control for enhanced precision. Advantages of Servo Motor Screw Driving Systems Servo motor screw driving systems provide several advantages in automation: High Precision: They achieve micron-level accuracy, making them suitable for tasks like semiconductor manufacturing and medical device assembly. Fast Response: Servo motors respond quickly to changes in load and speed, improving cycle times in production. Energy Efficiency: These systems consume power only when in motion, reducing operational costs. Low Maintenance: Closed-loop mechanisms minimize wear and tear, ensuring long-term reliability. Applications of Servo Motor Screw Driving Systems These systems are used across various industries, including: CNC Machining: For precise tool positioning in milling and cutting operations. Packaging Machinery: Ensuring accurate product placement and sealing. Robotics: Enabling smooth and controlled movements in robotic arms and assembly robots. 3D Printing: Delivering high-resolution layer deposition for additive manufacturing. Servo motor screw driving systems play a vital role in advancing automation by delivering speed, precision, and reliability. Whether in high-speed production or delicate assembly tasks, these systems enhance performance while reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs. Product Name Applicable industries Smart Screw Driving Machine PCB and Circuit Board Assembly
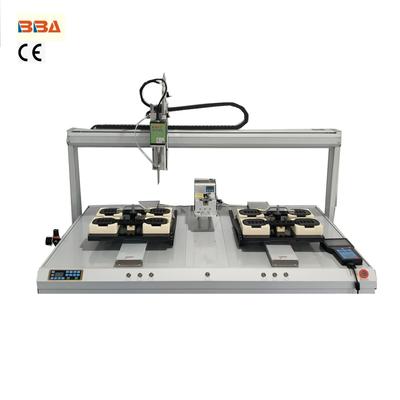

Popular Screw Tightening Models in India and Southeast Asia The demand for precision and efficiency in industrial automation has driven the adoption of advanced screw tightening solutions across India and Southeast Asia. These tools play a crucial role in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, electronics, and machinery assembly. Below, we explore some of the most popular screw tightening models in these regions, highlighting their features and applications. 1. Ergonomic Electric Screwdrivers Electric screwdrivers with ergonomic designs are widely used for high-volume assembly lines. Their lightweight construction reduces operator fatigue, while programmable torque settings ensure consistent fastening quality. These models are particularly popular in India's electronics manufacturing sector, where precision is critical for delicate components. 2. Industrial Pulse Tools Pulse tightening tools are favored in Southeast Asia's automotive industry for their high-speed performance and energy efficiency. These models deliver rapid bursts of torque, making them ideal for repetitive tasks in engine assembly and chassis construction. Their compact size allows access to tight spaces while maintaining high torque output. 3. Smart Cordless Screwdrivers Cordless models with Bluetooth connectivity have gained popularity across both regions. These tools offer real-time data monitoring and can integrate with production tracking systems. Manufacturers appreciate the combination of mobility and digital capabilities for quality control in large-scale operations. 4. Multi-Spindle Tightening Systems For high-throughput applications, multi-spindle systems automate the tightening of multiple screws simultaneously. These are extensively used in appliance manufacturing throughout Southeast Asia, dramatically improving cycle times while maintaining uniform clamping force across all fasteners. 5. Robotic Screw Tightening Cells As factories embrace Industry 4.0, robotic tightening solutions are becoming standard in advanced manufacturing facilities. These automated cells combine vision systems with precision tightening for complex assemblies, particularly in India's growing aerospace and medical device sectors. The screw tightening technology market in India and Southeast Asia continues to evolve, with increasing demand for intelligent, connected tools that support digital manufacturing initiatives. Manufacturers should consider factors such as production volume, precision requirements, and integration capabilities when selecting the appropriate model for their operations. Product Name Applicable industries Desktop Screwdriver Robot Electric Bicycle Assembly
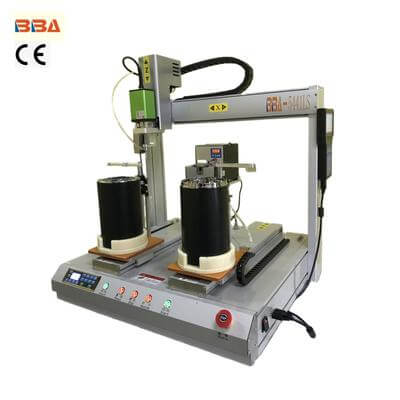

In the fast-paced world of industrial automation, minimizing downtime during product changeovers is critical to maintaining productivity and competitiveness. A quick product changeover ensures that your production line can adapt to new product specifications with minimal disruption. This article explores key strategies to achieve efficient changeovers in industrial automation settings. 1. Standardize Changeover Procedures Developing standardized procedures is the foundation of efficient changeovers. Document every step, from dismantling current setups to configuring new parameters. Use clear checklists and visual guides to reduce human error and ensure consistency. Automation software with pre-programmed changeover sequences can further streamline the process. 2. Implement Modular Design Modular equipment design allows for rapid component swaps. Consider using quick-connect interfaces, standardized fixtures, and tool-less change mechanisms. Color-coding components for different product lines can help operators identify correct parts quickly, reducing changeover time significantly. 3. Optimize Material Preparation Prepare all necessary materials, tools, and components before initiating the changeover. A well-organized staging area near the production line ensures everything is within reach. Automated material handling systems can be programmed to deliver required components just in time for the changeover. 4. Leverage Advanced Controls Modern industrial controllers can store hundreds of product recipes. Implementing recipe management systems allows for one-touch changeovers where machines automatically adjust parameters. Consider integrating vision systems or RFID technology for automatic product identification and configuration. 5. Train and Cross-Train Personnel Skilled operators are essential for quick changeovers. Regular training sessions and simulations help teams perfect changeover techniques. Cross-training ensures multiple staff members can perform changeovers, increasing flexibility in production scheduling. 6. Continuously Improve Processes Use time-motion studies to identify bottlenecks in your changeover process. Implement lean manufacturing principles like SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) to convert internal changeover tasks to external ones. Regular reviews of changeover performance can reveal opportunities for further optimization. By implementing these strategies, industrial automation facilities can achieve remarkable reductions in changeover time. The benefits extend beyond time savings to include improved equipment utilization, greater production flexibility, and the ability to respond quickly to market demands. Remember that successful quick changeovers require both technological solutions and well-trained, motivated personnel working together as a team. Product Name Applicable industries Auto Screwdriver Machine Power Tool Assembly Lines
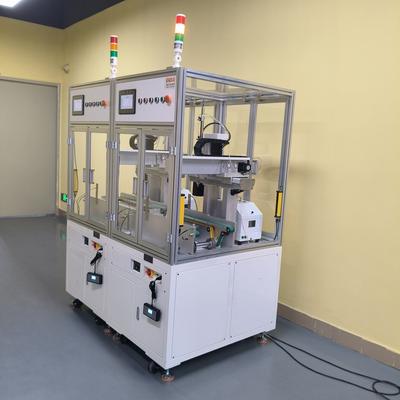

In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the ability to handle mixed-model production efficiently has become a critical competitive advantage. Multi-axis robots are emerging as a game-changing solution, enabling manufacturers to adapt quickly to varying product designs, sizes, and specifications without costly retooling or downtime. The flexibility of multi-axis robotic systems allows seamless transitions between different product models on the same production line. Unlike traditional single-purpose automation, these advanced robots can perform complex tasks such as material handling, assembly, and packaging across diverse product variations with minimal reprogramming. Key Benefits of Multi-Axis Robots for Mixed-Model Production 1. Adaptive Programming Modern robotic controllers support dynamic program switching, allowing immediate adaptation to different product specifications. This capability significantly reduces changeover times between production runs. 2. Precision Handling With multiple degrees of freedom, these robots can manipulate components of varying shapes and sizes with sub-millimeter accuracy, maintaining quality standards across all product variations. 3. Space Optimization The compact workspace requirements of multi-axis systems enable manufacturers to implement flexible production cells that can handle multiple product types without expanding floor space. Implementation Considerations When integrating multi-axis robots into mixed-model production environments, several factors should be considered: Standardized interfaces for quick tool changes Advanced vision systems for part identification and localization Scalable control architecture to accommodate future product variations Collaborative safety features for environments with human workers The integration of machine learning algorithms further enhances the capabilities of multi-axis robotic systems. Predictive analytics can optimize task sequencing and motion paths for different product models, continuously improving efficiency over time. As consumer demand for product variety continues to grow, manufacturers leveraging multi-axis robotic solutions will be better positioned to maintain profitability while meeting market expectations for customization and rapid delivery. The future of manufacturing belongs to those who can combine the precision and speed of automation with the flexibility to handle diverse product portfolios seamlessly. Multi-axis robotic systems represent a significant step toward achieving this vision in modern industrial environments. Product Name Applicable industries Automatic Screw Feeder Smart Wearables Production
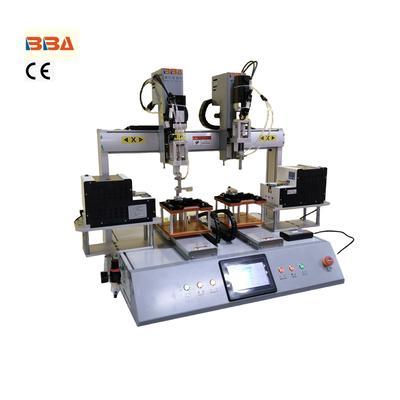

Desktop vs. Inline Screw Robots: Which One Suits You? In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, precision and efficiency are non-negotiable. Screw fastening robots have become indispensable for industries aiming to optimize assembly processes. Two popular solutions – desktop and inline screw robots – offer distinct advantages depending on operational requirements. Let’s explore their differences to help you make an informed decision. Desktop Screw Robots: Compact Precision Ideal for limited-space environments, desktop models feature: Space-saving footprint (under 1m² typical) Rapid deployment for small-batch production Operator-friendly programming interfaces Best suited for prototyping, R&D labs, or low-volume manufacturing requiring frequent product changeovers. Inline Screw Robots: High-Speed Automation Designed for seamless production line integration: Synchronized parts handling via conveyors Throughput exceeding 40 cycles/min Automated error detection systems The optimal choice for mass production scenarios where uptime and consistency are critical. Key Decision Factors Production Volume: Desktop (≤5,000 units/day) vs. Inline (10,000+ units/day) Floor Space: Desktop requires 60% less installation area Flexibility: Desktop allows faster retooling (under 30 mins typical) ROI Timeline: Inline systems typically payback in 12-18 months at scale Hybrid Solutions Emerging Latest modular designs now enable: Desktop-to-inline configuration upgrades Dynamic torque adjustment algorithms Cross-platform software integration Pro Tip: Conduct a cycle time analysis and 5-year production forecast before deciding. Many operations benefit from combining both types in different production stages. Selecting the right screw robot type directly impacts your operational efficiency and bottom line. While desktop units excel in flexibility, inline systems dominate in high-volume scenarios. Evaluate your current needs while accounting for future scalability to make a choice that grows with your business. Product Name Applicable industries Auto Screwdriver Machine Smartphone Manufacturing
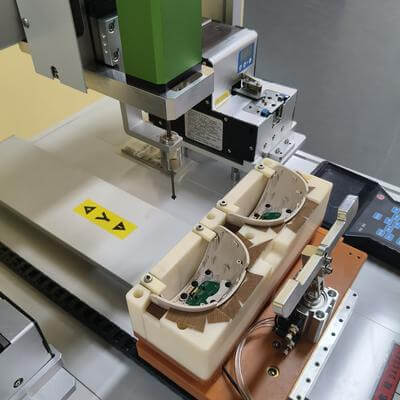

Key Components of a Robotic Screw Driving System As industries evolve, the demand for precise, efficient, and reliable automation solutions has never been higher. One of the cornerstone components in many automation setups is the robotic screw driving system. Essential in countless applications, from automotive assembly to electronics manufacturing, robotic screw driving systems enhance the accuracy, speed, and consistency of operations. This comprehensive guide delves into the vital components that constitute a robotic screw driving system, exploring their functions, importance, and interdependencies. 1. Robotic Arm At the heart of any robotic screw driving system is, predictably, the robot itself, often referred to as a robotic arm. The robotic arm performs the mechanical movements required for driving screws. It is crucial to select an arm with the proper precision, payload capacity, and range of motion to match the specific application requirements. In many cases, an articulated robot, with its swivel-like joints and wide range of motion, would be most suitable for complex operations. Alternatively, a Cartesian robot, with its linear movements across the X, Y, and Z axes, might be ideal for straight-line screw driving tasks. 2. End-of-arm Tooling (EOAT) End-of-arm tooling is another crucial aspect of robotic screw driving systems. EOAT, an attachment fitted to the end of the robotic arm, comprises various tools, fixtures, or devices to perform specific tasks. In the context of screw driving, EOAT configurations may include screwdrivers, nutrunners, or custom-made tools. The ability to change EOAT quickly and efficiently, often through automated tooling changers, allows for versatile and flexible robotic solutions, catering to diverse product lines or varying production demands. 3. Screw Feeding Mechanism The smooth feeding of screws into the robotic system is integral to efficient operations. Numerous screw feeding mechanisms are available, including vibratory bowls, auger feeders, and linear screw feeders. Each feeding method has its benefits and limitations, depending on the screw geometry, production rate, and cost considerations. Integrating an efficient screw feeding mechanism with the robotic system ensures a reliable supply of screws and reduces instances of missed screws, which could lead to assembly errors. 4. Vision System In many cases, a vision system may be necessary to guide the robotic screw driving process. Vision systems utilize cameras, image processors, and algorithms to detect and interpret visual input. In a robotic screw driving application, vision systems help locate and recognize screw locations, identify screw types, and monitor screw fastening quality. Advanced vision systems can detect and adapt to variations in component positioning and compensate for minor discrepancies in real time, ensuring consistently accurate results. 5. Control System and Software The control and software systems provide the brainpower to coordinate a robotic screw driving system effectively. They are responsible for programming, sequencing, motion control, and communication with other production systems. Sophisticated software packages often include graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and intuitive programming features to make setup and operation straightforward, even for non-engineering users. Integrating control system functionalities, such as torque feedback and process monitoring, helps safeguard against errors and optimizes the performance of the robotic system. 6. Safety Interlocks and Protective Measures Finally, ensuring a safe operating environment is an indispensable aspect of any robotic screw driving system. Protective measures may include safety cages, laser scanners, and interlocked access doors to mitigate the risk of injury to human operators. Implementing safety interlocks, such as force-limiting or speed-limiting features, helps to prevent excessive forces that might damage components or compromise quality. Robotic screw driving systems have become a crucial aspect of many manufacturing and assembly processes. To assemble a reliable, efficient, and safe robotic screw driving system, one must balance and integrate the key components discussed above, fine-tuning their interactions and operation as per the application's specific needs. By leveraging the latest in robotics and automation technologies, businesses can capitalize on the myriad benefits offered by these advanced systems to optimize productivity, quality, and overall competitiveness. Product Name Applicable industries Automatic Screw Feeder Medical Device Manufacturing

Product Name Applicable industries Servo Screwdriver Robot Automotive Electronics Assembly Automation and Labor Efficiency in Global Markets In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the integration of automation technologies has become a pivotal force in enhancing labor efficiency across global markets. As businesses navigate challenges such as workforce shortages, rising operational costs, and the need for scalable production, automation offers a transformative solution that reshapes productivity paradigms. This article explores how automation drives labor efficiency worldwide, enabling companies to achieve higher output, reduce errors, and maintain competitive advantage in an interconnected economy. Automation revolutionizes productivity by streamlining repetitive tasks that traditionally relied on manual labor. In manufacturing plants worldwide, intelligent systems handle assembly lines, quality control, and material handling with exceptional precision and speed. For instance, robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors can operate 24/7, significantly boosting output while minimizing errors related to human fatigue. This efficiency translates to shorter production cycles and lower costs, allowing businesses to allocate human workers to more strategic roles that demand creativity and problem-solving. Thus, automation doesn't eliminate jobs but elevates labor to higher-value activities, fostering a workforce that is more engaged and productive. On a global scale, automation empowers companies to standardize operations across diverse regions, ensuring consistent quality and reliability. In markets facing demographic shifts or skill gaps—such as aging workforces in developed nations or emerging economies with high labor turnover—automation provides a stable solution. By deploying modular systems that adapt to local needs, organizations can scale efficiently without overwhelming manual inputs. This not only addresses unpredictability in labor availability but also enhances business continuity, as automated processes are less prone to disruptions from events like pandemics or geopolitical tensions. Consequently, labor efficiency improves through optimized workflows, where automated analytics track performance in real-time, enabling data-driven decisions that fine-tune resource allocation globally. Moreover, investing in automation yields long-term savings that strengthen sustainability and competitiveness. While initial implementation requires capital, the return on investment becomes evident through reduced waste, energy consumption, and labor overheads. Automated systems optimize material usage and predict maintenance needs, preventing costly downtime. In global supply chains, this efficiency enhances speed-to-market, helping companies meet fluctuating demands and maintain market share. For labor forces, automation fosters skill development, as workers learn to manage and maintain advanced technologies, thus building a future-proof workforce. This holistic approach ensures that labor efficiency is not just about cutting costs but creating resilient operations that thrive in the face of market uncertainties. In conclusion, automation is indispensable for elevating labor efficiency in global markets, driving innovation and profitability. By embracing these technologies, businesses can harness unprecedented productivity gains, adapt to diverse labor landscapes, and achieve sustainable growth. As the industry progresses, leveraging automation solutions remains key to unlocking human potential and securing a competitive edge in the worldwide economy.
Product Name Applicable industries Screw Locking Robot Power Tool Assembly Lines For industrial automation companies specializing in screw fastening equipment, mastering Google search visibility requires strategic keyword targeting. Effective SEO begins with understanding precisely what potential customers search for when seeking these specialized solutions. This guide outlines essential keyword categories to elevate your screw fastening machines in search rankings. Core Product Keywords are fundamental. Prioritize terms like "automatic screw fastening machine," "industrial screwdriving system," and "robotic screw tightening equipment." These short-tail phrases capture broad search intent, helping establish your relevance in the automation landscape. Complement them with variants such as "electric screw feeder," "pneumatic screwdriver machine," and "multi-spindle fastening system" to cover diverse technical specifications. Long-Tail & Solution-Oriented Keywords address specific pain points and applications. Queries like "high-speed PCB screw fastening solution" or "torque-controlled automated screwdriver for electronics assembly" signal strong commercial intent. Integrate usage scenarios: "automated screw insertion for automotive manufacturing," "desktop screw fastening machine for small parts," or "ergonomic screwdriver system for production lines." These phrases connect with niche buyers and typically face less competition. Don’t overlook Commercial Modifiers. Terms like "custom screw feeding system manufacturer," "industrial screw presenter price," "CNC screw fastening machine supplier," and "buy automatic screwdriver online" indicate users nearing purchasing decisions. Including modifiers such as "reliable," "low maintenance," or "high-accuracy" further qualifies leads by emphasizing your equipment’s unique value. Localized Keywords boost regional visibility. Combine service areas with core terms: "screw fastening automation company Germany," "automated screwing machine supplier California," or "screw feeder integration services Japan." For immediate proximity traffic, optimize for "automated screwdriver near me" and "industrial fastening systems near me" – critical for service teams targeting manufacturers. Tech-Specific Keywords attract informed buyers. Target precision-oriented phrases: "closed-loop torque control screwdriver," "vision-guided robotic screw insertion," or "servo-driven fastening system." Mentioning capabilities like "error-proofing," "MES connectivity," or "feed time optimization" appeals to engineers prioritizing advanced functionality. As voice search grows, adapt to Natural Language Phrases like "best screw assembly machines for HVAC production" or "how an automatic screw feeder reduces operator fatigue." Embed question-based terms: "why use servo-electric screwdrivers?" or "how to improve screw fastening cycle times?" to align with spoken queries and featured snippets. Consistently analyze keyword performance through Google Analytics and Search Console. Track queries driving conversions – especially "high torque screw fastening system for sale" or "XYZ model specifications." Monitor emerging trends like "collaborative robot screwdriver integration" to stay ahead. Successful SEO requires balancing high-volume terms for visibility and solution-driven phrases for qualified leads, adapting continuously as industrial automation evolves. A dynamic, context-rich keyword strategy positions your screw fastening technology at the forefront – transforming searches into tangible industrial partnerships.